What Is a Flat Laser?
A flat laser refers to a laser system that produces a flat-top beam profile instead of a traditional Gaussian beam profile. In simple terms, this means the laser beam maintains uniform intensity across the entire diameter, rather than being strongest in the center and fading toward the edges.
This uniformity is important for applications that require consistent heat distribution, such as cutting, welding prep, and die cutting. By delivering the same energy across the beam, flat lasers produce cleaner cuts, sharper edges, and less material distortion compared to conventional laser systems.
How Does a Flat Laser Work?
Flat lasers achieve their uniform beam profile through beam shaping technology. Using diffractive beam shapers or other optical components, the electric field of the beam is manipulated so that energy is distributed evenly rather than peaking at the center.
Key components include:
- Laser Source: Generates the initial beam.
- Beam Shapers: Refractive or diffractive optics reshape the beam into a flat-top profile.
- Finite-Sized Cavity Design: Maintains stability of the beam profile during operation.
This configuration eliminates “hot spots” that can cause uneven cutting or material distortion, making flat lasers ideal for producing high-quality, consistent results.
What Is the Difference Between a Flat Laser and a Gaussian Laser?
The main difference between a flat toplaser and a Gaussian laser lies in their beam profiles.
- Flat Top Beam: Produces a flat-top beam profile where energy is evenly distributed across the beam. This uniformity allows for consistent cutting depth, cleaner edges, and reduced thermal stress on the material.
- Gaussian Beam Profiles: Has a peak intensity at the center of the beam and gradually decreases toward the edges. This uneven energy distribution can cause localized overheating, resulting in rough edges, heat-affected zones, and inconsistent cut quality.
Why does this matter? For manufacturers working with thin sheet metal, intricate designs, or advanced materials, flat lasers provide greater control and higher precision. Gaussian beams may still be effective for less demanding tasks, but they often require additional finishing work.
Why Use a Flat Laser Instead of a Gaussian Laser?
Flat lasers provide several performance advantages over traditional Gaussian lasers:
- Uniform Energy Distribution: Reduces thermal stress and produces cleaner cuts.
- High Accuracy and Precision: Consistent energy means precise edge quality for intricate designs.
- Cleaner Edges and Reduced Finishing: Cuts have minimal burrs and often require less post-processing.
- Material Versatility: Works well on stainless steel, mild steel, aluminum, and thin films.
These benefits make flat lasers a reliable option for projects requiring sharp edges, tight tolerances, and repeatability.
How Accurate Is Flat Laser Cutting?
Flat laser cutting is known for its high accuracy and high precision, often reaching tolerances as tight as ±0.005 inches. The flat-top beam profile ensures that energy distribution remains consistent across the cut path, which is particularly important for components with intricate shapes or tight dimensional requirements.
This level of precision is ideal for:
- Industrial Components that need exact dimensions for proper assembly.
- Prototyping where accuracy determines performance.
- Medical Devices where consistency is essential for safety and functionality.
By reducing thermal variation, flat lasers also minimize distortion, allowing parts to maintain their intended geometry without extensive secondary processing.
What Materials Can a Flat Laser Cut?
Flat lasers are versatile and can cut a wide range of materials, including:
- Stainless Steel: Used in industrial machinery, food processing equipment, and medical tools.
- Mild Steel: Common in construction, automotive, and heavy equipment manufacturing.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and strong, often used in aerospace and transportation.
- Thin Films and Coatings: Found in electronics and advanced material applications.
- Composite Sheets: Utilized in specialized industrial and engineering projects.
This flexibility allows manufacturers to use flat lasers across multiple sectors, from heavy-duty industrial work to delicate high-tech components.
Can a Flat Laser Cut Thick Material?
Yes, flat lasers can cut both thin and thick materials, depending on the power of the laser source and setup configuration. While they excel in cutting thin sheet metal and films, they are also capable of working with thicker sections of steel or aluminum when equipped with the appropriate power settings.
However, for very thick materials, the cutting speed will decrease, and multiple passes may be required. In such cases, flat lasers still deliver cleaner, more precise cuts compared to traditional cutting methods, often reducing secondary finishing work.
Flat Laser Applications in Manufacturing
Flat laser systems are widely used across different industries due to their ability to deliver consistent performance. Some common applications include:
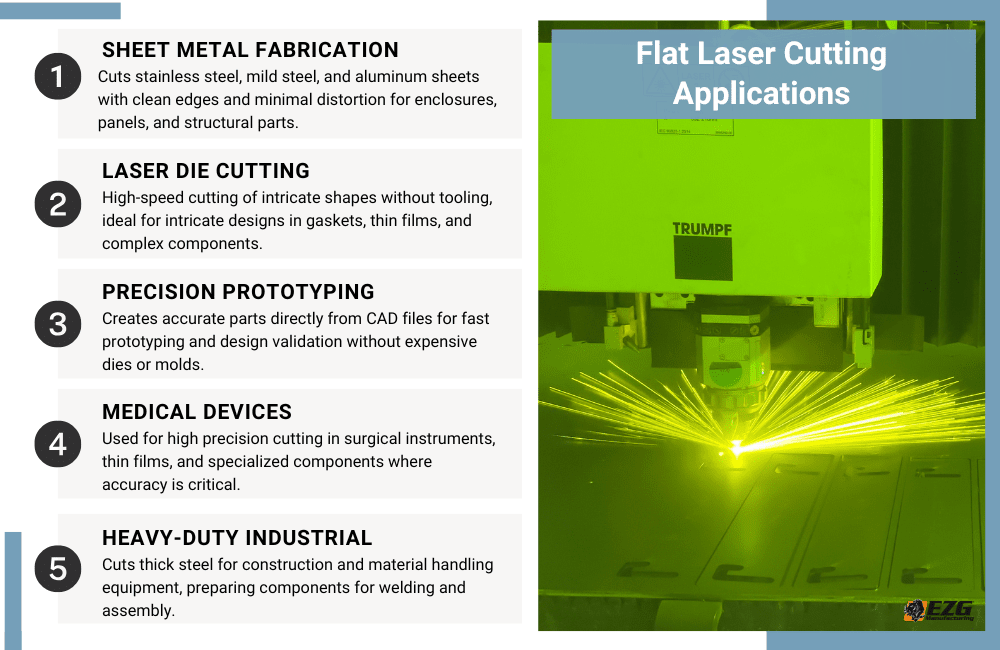
Sheet Metal Fabrication
One of the primary uses of flat lasers is in sheet metal fabrication, where they cut thin and medium-gauge metal sheets into precise shapes. These components often form the foundation of industrial equipment, control panels, and structural parts. Flat lasers can cut materials with minimal distortion, reducing the need for post-processing.
The flat-top beam profile plays an important role here, as it prevents excessive heat from concentrating in one area. This means cleaner edges, less warping, and higher repeatability across production runs. Flat lasers also excel at cutting intricate designs from large sheets, which makes them ideal for custom enclosures, machine frames, and architectural components.
Laser Die Cutting
Unlike traditional die cutting that requires custom tooling, laser die cutting uses programmed paths to cut material, which significantly reduces setup time and cost.
Manufacturers rely on flat lasers for high-speed cutting of components with intricate geometries, especially when tolerances are tight. Because there is no physical tool contact, the process eliminates wear and tear issues associated with mechanical dies, resulting in consistent quality throughout long production runs. Applications include gaskets, thin films, and metal inserts for various industries.
Precision Prototyping
Flat lasers allow manufacturers to cut prototype parts directly from digital files without creating expensive tooling. This capability makes them a popular choice for rapid prototyping. Their ability to handle complex shapes with tight tolerances means engineers can create fully functional prototypes that reflect final product specifications.
Medical and Advanced Applications
Flat lasers are used extensively in medical and advanced technology sectors because of their ability to produce clean, accurate cuts in delicate materials. They are employed to cut thin films and stainless steel parts for surgical instruments and medical devices, where precision and cleanliness are essential.
Beyond medical applications, flat lasers also support advanced manufacturing for electronics and aerospace, cutting intricate components from specialized alloys, thin foils, and composite materials. They are also critical in producing compliant mechanisms, which are flexible structures used in precision instruments and implants.
Heavy-Duty Industrial Use
Flat lasers also have a strong presence in heavy-duty industrial sectors like construction, agriculture, and material handling. These industries often require thick metal components that need to be cut accurately for welding and assembly. Flat lasers can handle large sheets of mild steel and stainless steel, preparing them for fabrication in structural frameworks, conveyor systems, and heavy machinery.
Their precision helps reduce alignment issues during assembly, while cleaner cuts minimize preparation work before welding or coating. In addition, flat lasers can create custom parts quickly for repair jobs or specialized equipment, reducing downtime in industries where productivity matters.
Flat Laser vs. Traditional Laser Cutting
| Feature | Flat Laser | Traditional Gaussian Laser |
|---|---|---|
| Beam Profile | Flat-top, uniform intensity | Peak center intensity |
| Cutting Accuracy | High, consistent across entire beam | Moderate, affected by hot spots |
| Edge Quality | Clean, sharp | May need additional finishing |
| Thermal Impact | Low, reduces warping | Higher, risk of heat distortion |
| Ideal Applications | Precision cutting, intricate designs | General cutting tasks |
Advantages of Using a Flat Laser in Contract Manufacturing
When compared to other cutting methods, flat lasers offer benefits that improve overall manufacturing quality:
- Cleaner Cuts and Sharper Edges
- Consistent Dimensional Accuracy
- Ability to work with high-speed production while maintaining detail
- Reduced finishing work due to improved edge quality
EZG Manufacturing and Flat Laser Capabilities
At EZG Manufacturing, our flat laser systems are part of a larger contract manufacturing operation that includes welding, machining, bending, and powder coating. This integrated approach allows us to take your project from design to finished product under one roof.
Our flat laser technology supports:
- Stainless steel, mild steel, and aluminum components
- High-precision parts for industrial, medical, and advanced applications
- Small runs and large-scale production projects
To learn more about how our flat laser capabilities can support your project, contact our contract manufacturing team today.