If you’re comparing billet vs forged parts, the short answer is this: forged parts are generally stronger due to the way their grain structure aligns during the forging process. However, the answer isn’t always black and white. While forged parts are often stronger in high-stress environments, billet parts offer better precision and flexibility for intricate or low-volume builds.
If you’re sourcing custom parts or planning a new build, understanding the differences between these two manufacturing methods can help you make the right decision. This guide breaks down everything you need to know.
What Is a Billet Part?
Billet parts are made by machining a shape or component from a solid piece of metal, referred to as a billet. These billets are typically pre-formed through casting or extrusion, and then milled, turned, or shaped using CNC (computer numerical control) machines.
How the Billet Manufacturing Process Works
The billet process starts with a raw, uniform metal block. Using CNC equipment, the part’s shape is cut away from this block in a subtractive process. This allows for extremely tight tolerances and detailed geometries.
Modern contract manufacturers use multi-axis CNC machines capable of producing repeatable, precise results across different material types.
Material and Structure
Billet material has a uniform, non-directional grain structure, meaning the internal arrangement of the metal is the same in all directions. This consistency offers good strength and predictability, especially for parts that don’t experience repetitive impact or high directional loads.
Typical materials used in billet machining include:
- Carbon steel
- Stainless steel
- Aluminum
- Specialty alloys
Unlike casting, where molten metal is poured into a mold, billet machining removes excess aluminum or steel until only the desired shape remains. This makes it ideal for parts that demand accuracy and uniformity.
Common Uses for Billet Parts
Because of the precision and customization available through CNC machining, billet parts are often the go-to choice for:
- Low-volume or one-off parts
- Aerospace or automotive prototypes
- Custom equipment requiring tight tolerances
- Parts with intricate details or surface finish requirements
- Billet wheels and brackets in automotive customization
These applications often require specific dimensions, finishes, or threading that are easier to achieve through billet machining.
What Is a Forged Part?
Forging is a forming process that uses compressive force, often heat-assisted, to shape metal into the desired form. Unlike billet machining, which cuts material away, forging reshapes the original stock using pressure and force.
How Forged Parts Are Made
Metal is heated until it’s pliable, then placed into a die or shaped with powerful hammers or presses. There are several types of forging:
- Open-die forging – for large or custom shapes
- Closed-die forging – for high-volume, repeatable parts
- Rolled ring forging – for creating ring-like components
After forging, the part is close to its final shape. Some post-forging machining is usually required to meet exact specifications.
Forged Material Strength
One of the biggest advantages of forging is the grain flow. During forging, the internal grain structure of the metal follows the contour of the part. This directional grain flow improves fatigue strength, impact resistance, and durability under stress.
Forged parts generally have greater strength than billet ones in dynamic or load-bearing environments. That’s why forging is often the go-to for heavy-use components.
Materials commonly forged include:
- Alloy steels
- Stainless steels
- Aluminum
- Titanium
Heat treatment is often used after forging to further improve the part’s mechanical properties.
When Forging Is the Better Choice
Forged components are typically found in areas where strength and durability matter most, including:
- High-volume production
- Applications with repetitive stress or impact
- Structural components in oil & gas, automotive, and construction
- Equipment subjected to high pressure or vibration
- Forged cranks and rods in automotive engines
These parts take on high loads, repetitive stress, and sometimes even extreme temperatures. Forging helps these parts last longer without failure.
Billet vs Forged vs Casting Process (Quick Overview)
Casting is another manufacturing method that involves pouring molten metal into a mold. It allows for complex shapes and is commonly used in high-volume production.
However, cast parts typically have lower strength due to a less uniform grain structure and the potential for porosity or internal defects.
Comparing Strength: Billet vs Forged
Here’s how billet and forged parts compare in performance-related categories:
| Feature | Billet | Forged |
|---|---|---|
| Grain Structure | Non-directional (uniform) | Directional (follows part shape) |
| Tensile Strength | Good and consistent | Higher, especially under load |
| Fatigue Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Impact Resistance | Lower | Superior |
Forged parts generally outperform billet parts when it comes to absorbing shock or withstanding repetitive stress. That said, billet is still strong and more suitable when design complexity and surface finish matter most.
Machining & Tolerances
Precision & Finish
The billet machining process offers excellent surface finishes and precision. Because these parts are cut using CNC equipment, the final product can have extremely tight tolerances, down to thousandths of an inch.
Forged parts, on the other hand, require additional machining to hit those same specs. While the forging process delivers strength, it can introduce surface irregularities or slight dimensional shifts that need cleanup.
Design Flexibility
CNC-machined billet parts are easier to modify mid-project. If you need a prototype or want to make minor design tweaks between versions, billet machining allows more flexibility. Forging, by contrast, is more fixed. You’re committed to the die shape once it’s made.
Which One Should You Use?
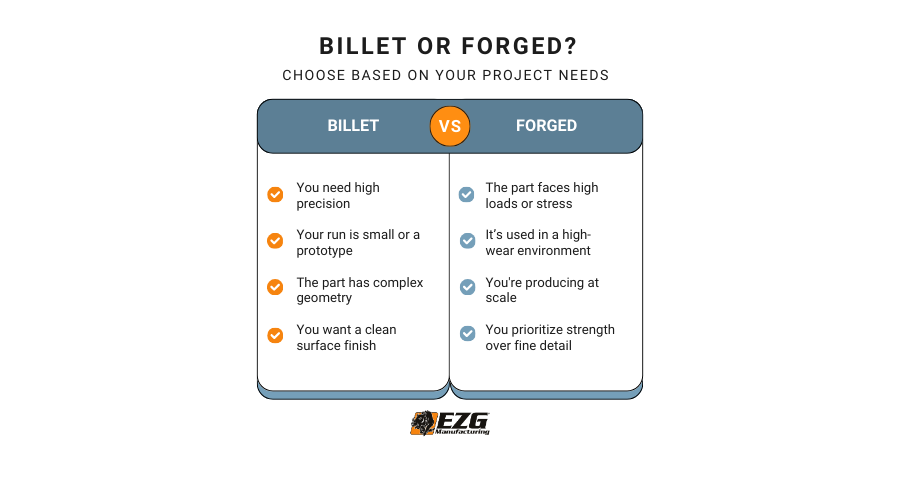
Still unsure which is right? Here’s a general breakdown based on use case:
Choose Billet if:
- You need high-precision parts
- Your project involves small runs or prototypes
- The component has complex geometry
- You want a clean surface finish straight off the machine
Choose Forged if:
- The part will face high loads or repetitive stress
- It’s going into a high-wear environment
- You’re manufacturing at scale and want long-term durability
- Strength is more important than fine detail
Cost Considerations
Here’s how billet and forged parts stack up in terms of production cost:
| Factor | Billet | Forged |
|---|---|---|
| Tooling Investment | Low | High (requires dies) |
| Material Waste | Higher (machining removes metal) | Lower |
| Labor Time | Higher per unit | Lower per unit in volume |
| Best For | Small runs or custom parts | Large runs with repeatability |
If you’re doing small batch work, billet machining may be more cost-effective. For larger volumes, forging becomes more efficient per part.
Manufacturing Considerations & CNC Machining
Whether you’re working with billet aluminum or a forged steel blank, CNC machining is often the final step that brings the part to spec. Billet material is easier to machine in detail, but forged material can still meet the same specs, just with more effort.
Both methods can benefit from post-processing such as powder coating or wet painting for protection and aesthetics, especially for parts exposed to wear, weather, or corrosive environments.
The Role of Contract Manufacturing in Choosing the Right Process
The right manufacturing partner won’t just ask what part you need, they’ll ask how you intend to use it. A strong fabrication and machining team can help:
- Analyze production volume needs
- Select the appropriate material and process
- Identify ways to reduce waste or improve turnaround
- Guide design adjustments for manufacturability
By understanding both the technical requirements and your business goals, a good partner can deliver solutions that work in the real world, not just on paper.
Partner with EZG for Both Billet and Forged Projects
EZG Manufacturing brings decades of experience in precision fabrication and machining. Whether your job calls for billet parts or forged components, we’ve got the team, tools, and technology to make it happen.
We specialize in built-to-print contract manufacturing for industries where performance, accuracy, and durability are non-negotiable.
Whether your project starts with billet bar stock or a forged blank, we have the capabilities to deliver:
- Laser cutting using high-speed fiber systems
- Precision CNC machining for tight-tolerance parts
- AWS-certified MIG and TIG welding
- Powder coating and wet painting for lasting finishes
- Large-part fabrication with 15-ton lifting capacity and 13 feet under the hook
From custom engine parts to high-stress industrial components, we produce parts that meet real-world demands—and we do it 90–95% in-house for better lead times and tighter control.
Ready to bring your billet or forged part to life?
Contact EZG Manufacturing to speak with our contract manufacturing team today.