Every product on your desk, in your garage, or rolling down a highway has something in common. It started on an assembly line. From the earliest machines of the Industrial Revolution to today’s automated production floors, assembly lines have shaped how the world builds, assembles, and delivers goods.
Below, we’ll go into how assembly line equipment improves output, reduces downtime, and supports modern manufacturing processes.
What Is Assembly Line Equipment?
An assembly line is a series of organized workstations where machines and operators perform repetitive tasks to create a finished product. Each stage contributes a specific step in the production process, moving materials efficiently from start to finish.
Assembly line equipment is the machines and tools that make these steps possible. Depending on the industry, this can include:
| Equipment Type | Function | Example Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Conveyor Belts | Moves products or parts between stations | Material transport in packaging, automotive, or food processing |
| Automated Assembly Machines | Performs fastening, soldering, or welding | Electronics, appliances, tools |
| Safety Equipment | Protects team members and machinery | Barriers, light curtains, sensors |
| Inspection Tools | Conducts in-line quality control | Vision systems, scanners, measuring devices |
| Packaging Systems | Prepares products for shipment | Box sealers, labeling machines |
Early versions of these systems emerged when interchangeable parts allowed mass production. Today, modern manufacturing combines those same ideas with automation and digital systems to achieve precision, speed, and repeatability.
The Role of Assembly Lines in Modern Manufacturing
The manufacturing industry depends on controlled processes that convert raw materials into reliable products. An assembly line makes this possible by organizing production into defined, repeatable steps.
Modern production lines are designed for:
- Consistency: Each product assembly line follows the same specifications to produce uniform results.
- Speed: Moving materials with conveyor systems eliminates idle time between stages.
- Scalability: Facilities can increase or decrease output by adjusting cycle times or adding equipment.
- Safety: Built-in protection for team members and machinery reduces accidents.
From metal fabrication and automotive manufacturing to food processing and electronics assembly, production lines allow factories to handle repetitive tasks efficiently and with accuracy.
How Assembly Line Equipment Improves Output
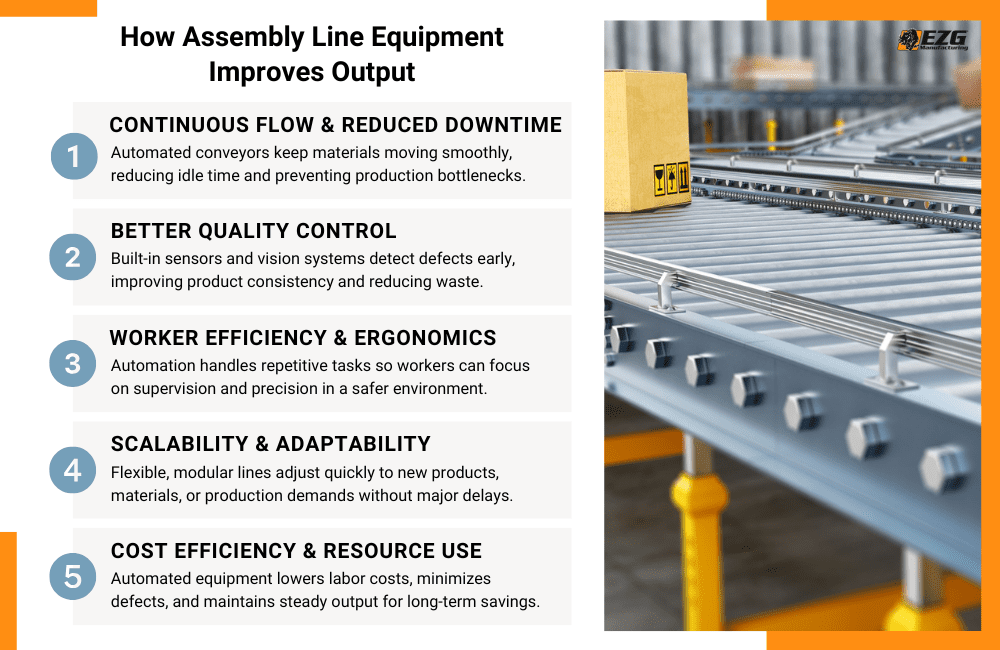
1. Continuous Flow and Reduced Downtime
One of the biggest benefits of assembly line equipment is the creation of a continuous flow. In a traditional setup, workers manually transport materials from one station to another. On a modern line, conveyor belts or automated assembly systems move materials automatically, eliminating wasted motion.
This consistent flow prevents backups and keeps each workstation operating at the same pace. Conveyor systems also make it easier to identify bottlenecks, as materials arrive exactly when needed.
Custom conveyor systems can be configured for different speeds, load capacities, and layouts, allowing manufacturers to meet unique production needs without halting the line.
2. Better Quality Control
Automation gives manufacturers greater control over product consistency. Sensors, scanners, and cameras positioned along a line can inspect components for defects before they reach final assembly.
For example:
- In metal fabrication, sensors confirm weld penetration and alignment.
- In electronics, automated testers verify circuit board function.
- In packaging, vision systems detect incorrect labeling or missing seals.
This integration of technology reduces human error and improves the reliability of every finished product. By catching issues early, companies minimize scrap, rework, and warranty costs, saving both time and materials.
3. Worker Efficiency and Ergonomics
Assembly line automation doesn’t replace people, it supports them. By assigning repetitive, physically demanding, or hazardous work to machines, team members can focus on supervision, quality checks, and process adjustments.
Ergonomically designed stations reduce strain and fatigue, while safety equipment and guards protect workers from moving parts. This approach creates a healthier work environment and sustains productivity over longer shifts.
When humans and machines work together efficiently, output rises naturally. Automation performs the repetitive task; people handle judgment and decision-making (tasks that match their strengths).
4. Scalability and Adaptability
Manufacturing rarely stands still. Product designs evolve, customer demand fluctuates, and materials change. Flexible assembly lines let manufacturers adapt quickly.
Using programmable logic controllers, adjustable conveyors, and modular workstations, factories can reconfigure their layout to build different products or handle various production equipment.
For example:
- A line making small parts can shift to larger assemblies by widening conveyor lanes.
- A welding process station can be reprogrammed for new materials or joint types.
- A multi-purpose automation equipment cell can perform fastening today and inspection tomorrow.
Flexibility like this keeps production stable during seasonal fluctuations or when introducing new designs.
5. Cost Efficiency and Resource Use
While investing in assembly machines and conveyors may seem expensive, the long-term payoff comes through lower labor costs, fewer defects, and less downtime.
By maintaining consistent cycle times, production becomes predictable. Automated equipment can operate longer hours without fatigue, and predictive maintenance systems identify issues before breakdowns occur.
Additionally, efficient production lines minimize space requirements. By organizing stations in sequence and using vertical or overhead conveyors, facilities can increase output without expanding their footprint.
The Role of Automation and Artificial Intelligence
Automation and artificial intelligence are redefining what a production line can achieve. Machines now handle complex decisions once reserved for people, improving speed and precision across every stage of the manufacturing process.
Examples include:
- AI-based vision systems that flag defects automatically
- Predictive maintenance sensors that monitor vibration, temperature, or wear on conveyor belts
- Automated assembly robots that adjust torque or weld time dynamically
- Adaptive scheduling software that adjusts shift plans based on material availability
Automation equipment doesn’t eliminate the human element; it augments it. When integrated with thoughtful assembly design, AI systems support smarter decision-making and more efficient use of labor.
Safety and Reliability in Assembly Equipment
Safety directly impacts output. A well-protected line operates longer and experiences fewer interruptions.
Modern industrial assembly setups incorporate:
- Emergency stop systems placed along conveyors
- Machine guarding to protect operators from moving components
- Automatic shutdowns triggered by overloads or obstructions
- Welding process enclosures that reduce heat and fume exposure
Regular inspection, cleaning, and calibration keep systems reliable. Manufacturers who prioritize preventive maintenance avoid unplanned downtime and keep production lines running consistently.
Durable assembly equipment, especially heavy steel frames and welded structures, plays an important role in longevity. Every weld, bearing, and drive component contributes to a dependable production environment.
Different Types of Assembly Line Equipment
Not every production facility uses the same setup. Equipment varies depending on material, product design, and required output. Here are some of the most common categories:
Manual Assembly Tools
Used for low-volume or specialized products that require hands-on attention. Examples include torque wrenches, rivet guns, and pneumatic presses.
Automated Assembly Machines
Perform consistent actions such as fastening, labeling, or soldering. Common in electronics, circuit board manufacturing, and appliance assembly.
Conveyor Systems

Move parts through the production process. These may include:
- Belt conveyors for steady material flow
- Roller conveyors for heavy items
- Overhead conveyors for space savings
Safety and Support Equipment
Includes guards, lighting, safety equipment, and quality control sensors that monitor product flow and worker protection.
Specialized Stations
Used for welding, painting, or material curing, especially in automotive or metal fabrication environments.
Designing an Efficient Assembly Line
An efficient line begins with good assembly design. The process typically involves:
- Analyzing production needs: Identify output goals, material type, and product size.
- Selecting the right equipment: Match assembly machines, automation equipment, and conveyor belts to the process requirements.
- Layout planning: Arrange stations for logical material flow, considering maintenance access and operator comfort.
- Testing and refinement: Run pilot batches, measure cycle times, and adjust for performance.
Attention to structure matters. Proper framing, accurate welds, and durable surfaces keep the system stable during high-speed operation. This is where fabrication expertise truly matters because design and build quality dictate longevity.
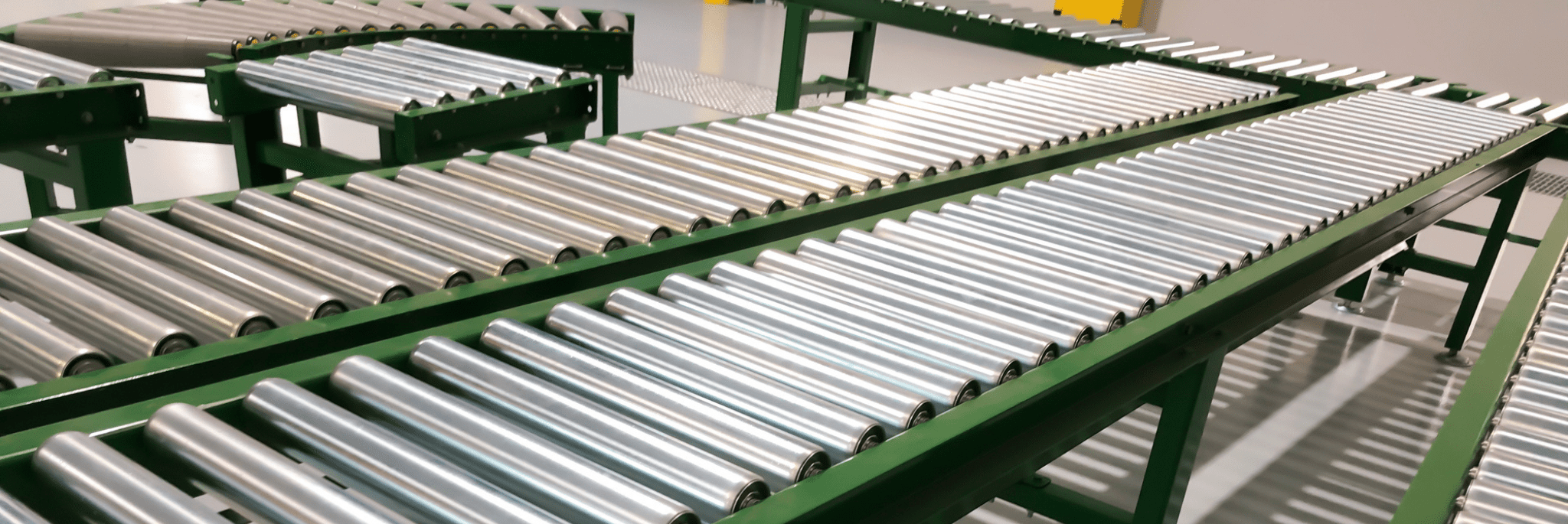
Conveyor Systems: The Backbone of Production Flow
In every assembly line, conveyor systems serve as the moving link that connects each stage of production. A well-built conveyor keeps the process synchronized, reduces manual handling, and protects components from damage.
Conveyors can be configured for nearly any application:
| Conveyor Type | Application | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Belt Conveyor | General material flow | Smooth, continuous transport |
| Chain Conveyor | Heavy-duty or irregular items | High load capacity |
| Roller Conveyor | Packaging or sorting | Easy product movement |
| Incline Conveyor | Vertical movement | Space-saving design |
Because they run continuously, reliability is everything. EZG Manufacturing specializes in designing and fabricating custom conveyor systems that integrate into complex production environments. With in-house welding and metal fabrication, EZG builds equipment that holds up under demanding workloads.
Why EZG Manufacturing Is a Trusted Partner
For over two decades, EZG Manufacturing has built its reputation on trust and durability. Our engineering and fabrication capabilities extend beyond standard equipment. They design complete solutions for industrial assembly and material handling.
Here’s what sets us apart:
- Complete fabrication under one roof: Every system is built under one roof, from frame welding to final inspection.
- Custom configurations: We tailor layouts to meet client-specific production needs. No cookie-cutter approach.
- Proven reliability: Our equipment supports continuous duty in demanding industries like masonry, construction, and material handling.
- Commitment to performance: Each conveyor is engineered for consistent throughput, minimal maintenance, and safe operation.
When a business needs dependable material flow and long service life, EZG provides the solution. Our team combines manufacturing knowledge with hands-on experience in assembly automation, industrial assembly, and process design.