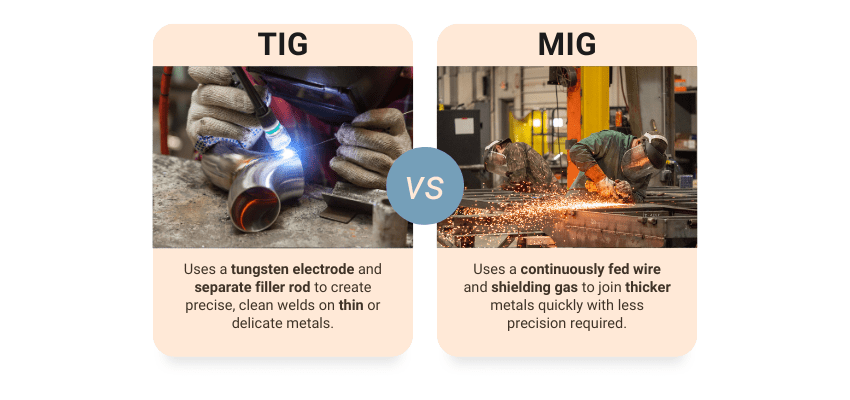
When you’re building a structure that needs to last or a component that needs to perform flawlessly, welding quality matters. The method you choose can affect everything from the final product’s strength to how it looks and how fast you can produce it. MIG and TIG are the two most common welding techniques, each with its strengths. This guide breaks down the differences so you can make the best decision for your next project.
What is MIG Welding?
MIG welding, short for Metal Inert Gas welding, is a process where a consumable wire electrode is continuously fed through a welding gun into the weld pool. An inert or semi-inert shielding gas, typically argon, carbon dioxide, or a mix, surrounds the weld area to protect it from atmospheric contamination.
This method is known for its speed and ease of use, especially when working with mild steel, carbon steel, or aluminum. Because of the continuous wire feed and fast travel speed, MIG welding is commonly used for projects involving thicker material and high production volumes.
MIG Welding Equipment
To perform MIG welding, the following components are typically used:
- MIG welder unit – the power source that controls voltage and current.
- Wire feed mechanism – continuously feeds the consumable wire electrode into the weld area
- Spool gun – often used when welding aluminum for better wire feeding performance.
- Shielding gas – protects the weld pool from contamination; usually a mix of argon and carbon dioxide, measured in cubic feet.
- Welding gun with trigger – allows the operator to control the arc and wire feed during welding.
Advantages of MIG Welding
- It allows for faster travel speeds, ideal for long welds or high-volume production.
- The process is easier to learn and operate compared to TIG welding.
- It performs well on thicker metals, such as structural steel or heavy-duty components.
- MIG welding can be semi-automated or fully automated, improving consistency and reducing operator fatigue.
- It requires less precise hand control, making it accessible to newer welders and faster to implement on the shop floor.
Common Applications
- Automotive and agricultural machinery, where speed and durability are critical.
- Structural steel fabrication for buildings, frames, and support components.
- Sheet metal work in HVAC systems, enclosures, and paneling.
- Metal gates, fences, and frames for both commercial and residential settings.
- Large-scale projects that involve repetitive welds and demand faster throughput.
What is TIG Welding?
TIG welding, or Tungsten Inert Gas welding, uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to generate an electric arc. The welder manually feeds a filler rod into the weld puddle while controlling the heat input through a foot pedal.
Unlike MIG, TIG welding doesn’t automatically feed filler material. This gives the operator greater control over the weld pool, making it ideal for jobs that demand a clean, smooth finish or involve thin metals like sheet metal, stainless steel, and aluminum.
TIG Welding Equipment
TIG welding uses a specialized set of tools and components to achieve precise and clean welds:
- TIG welder – a power source that provides adjustable current, allowing for fine-tuned control of the welding arc.
- Non-consumable tungsten electrode – creates the electric arc and maintains its shape during welding without melting into the weld pool.
- Foot pedal – used by the operator to control the heat input in real time, allowing for smoother starts, stops, and transitions.
- Filler rod – manually fed into the weld puddle by the welder to build up the joint as needed.
- Shielding gas – typically pure argon, used to protect the weld area from atmospheric contamination and maintain arc stability.
Advantages of TIG Welding
- It provides greater precision and control, making it suitable for intricate or delicate work.
- TIG is excellent for welding thin metals, such as sheet metal or fine stainless steel parts.
- The process allows for clean, high-quality welds with minimal spatter and excellent appearance.
- It gives the operator fine control over the weld puddle, thanks to manual filler feeding and foot pedal heat modulation.
- TIG welding is ideal for cosmetic welds or parts that must meet strict visual and dimensional standards.
Common Applications
- Aerospace components, where tolerances are tight and materials often include exotic alloys.
- Medical device fabrication which demands hygienic, defect-free welds.
- Food-grade stainless steel tanks and equipment, where smooth welds help avoid contamination.
- Custom ornamental or architectural metalwork, where the weld must blend in visually with the design.
- Precision fabrication projects where dimensional accuracy and strength are equally important.
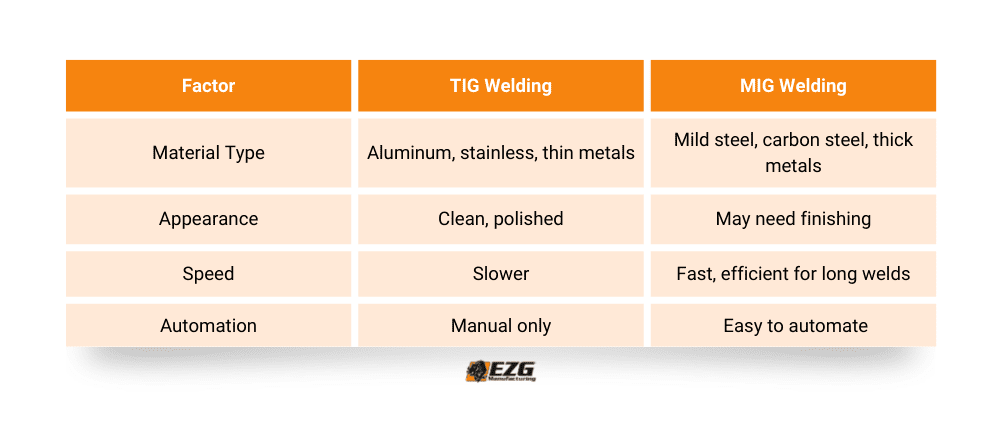
| Feature | MIG Welding | TIG Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Electrode Type | Consumable wire | Non-consumable tungsten |
| Filler Material | Fed automatically | Manually added with filler rod |
| Heat Input Control | Gun trigger | Foot pedal for precise adjustment |
| Speed | Fast | Slower |
| Skill Requirement | Easier to learn | Requires more experience |
| Best for | Thick materials, high-volume work | Thin metals, clean aesthetic welds |
| Shielding Gas | Argon, CO₂ mix | Pure argon |
| Surface Finish | May need post-weld cleanup | Clean, polished results |
| Automation Compatibility | Easily automated | Typically manual |
| Materials | Mild steel, aluminum, carbon steel | Stainless steel, aluminum, titanium |
How to Choose Between MIG and TIG Welding
If you’re unsure which process fits your project, consider these questions:
What kind of material are you welding?
- TIG welding is better suited for stainless steel, aluminum, and thin-gauge sheet metal.
- MIG works well with mild steel, carbon steel, and thicker material.
Does the weld need to look flawless?
- TIG produces clean welds with a polished appearance.
- MIG is more functional but may require additional finishing for a smooth look.
Is speed a priority?
MIG welding is significantly faster than TIG, especially for long welds or production runs.
Do you need automation?
MIG is easier to automate, making it suitable for robotic welding tasks like those handled by EZG’s Fanuc 120ic robotic cell.
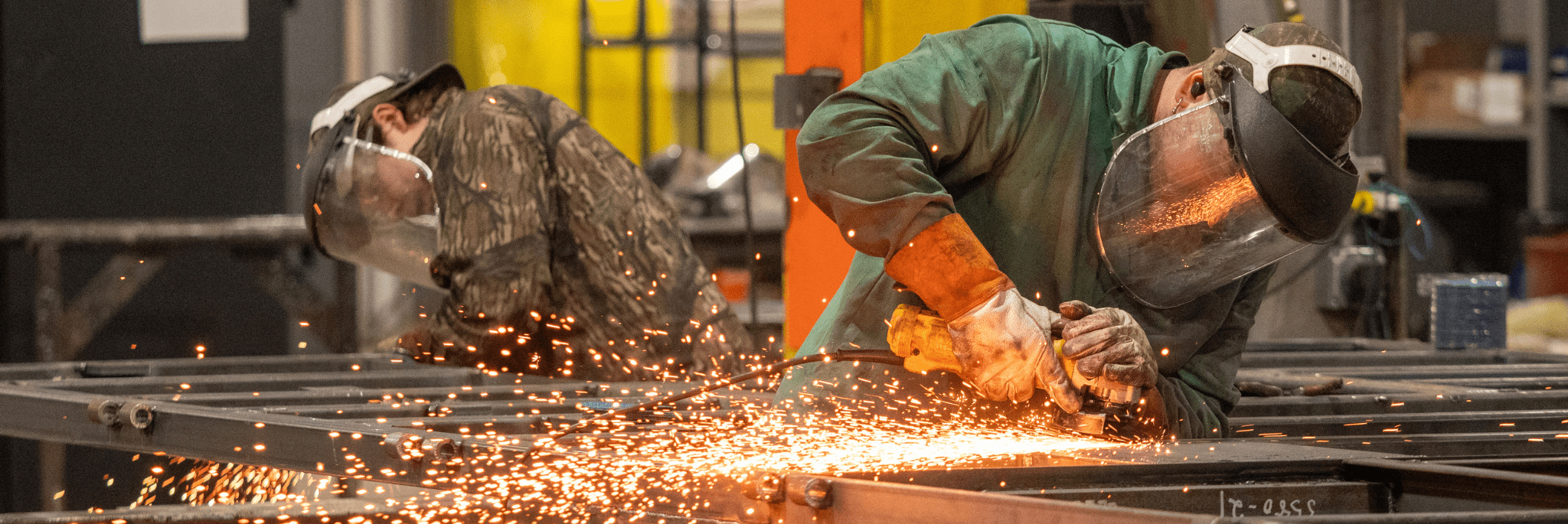
Welding at EZG Manufacturing
With over 25 years of experience and 120,000 square feet of fabrication space, our team at EZG Manufacturing provides built-to-spec welding solutions using both MIG and TIG methods. Whether you need rapid production or refined precision, we can deliver it in-house.
We offer both manual MIG and TIG welding for custom applications, as well as robotic welding using our FANUC 120ic cell for high-volume production runs. Our welders are AWS certified and experienced with materials like stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, and exotic alloys.
Because we’re a full-service shop, your project doesn’t leave our facility for other fabrication steps. From welding to powder coating, we handle it all internally. This helps us keep control of quality and timing from start to finish.
We work on everything from small, detailed brackets to large-scale structural steel. Weld integrity is always a priority, and we follow each specification with care. Our team is known for meeting tight deadlines without cutting corners, delivering consistent quality with every job.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use MIG welding on stainless steel?
Yes. With the right shielding gas and wire type, MIG is effective for stainless steel, especially when speed matters more than appearance.
Is TIG welding stronger than MIG?
TIG can produce stronger, more reliable welds when properly executed—especially for thin material or welds requiring greater precision.
What does a foot pedal do in TIG welding?
It lets the operator control the heat input in real time, allowing for smooth starts and stops without overheating the base metal.
Why is TIG welding slower?
Because the filler rod is added by hand and the arc is controlled with a foot pedal, TIG welding takes longer but produces a high-quality weld.
Reach Out to Find Out Which Welding Process is Right for Your Project
At EZG Manufacturing, we don’t believe in one-size-fits-all. Our team of certified welders and in-house robotic systems allows us to choose the right process for your job, delivering reliable results every time.
Need help choosing the right welding method for your project? Contact our team today and find out how EZG can build it to print, on time, and with the quality you expect.