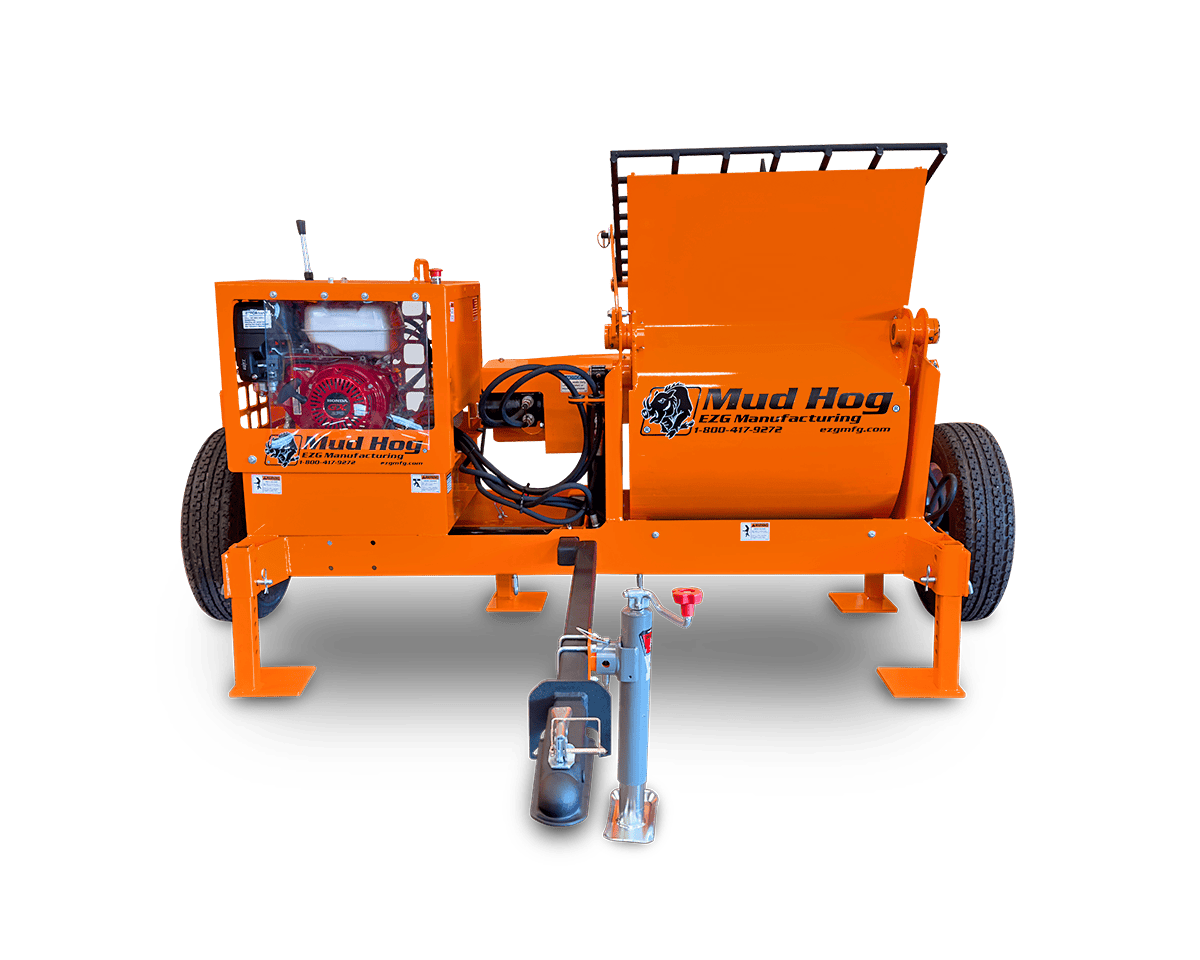
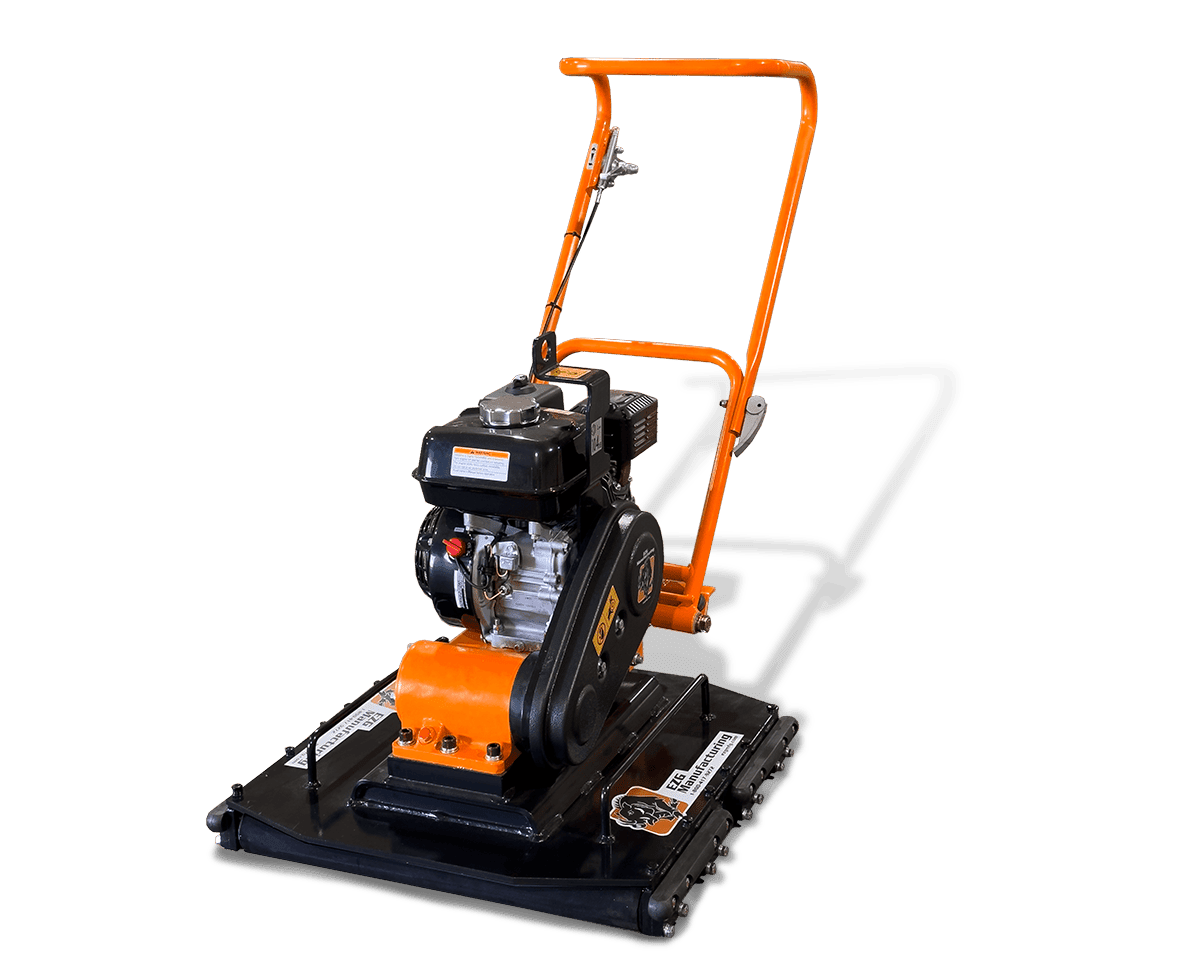
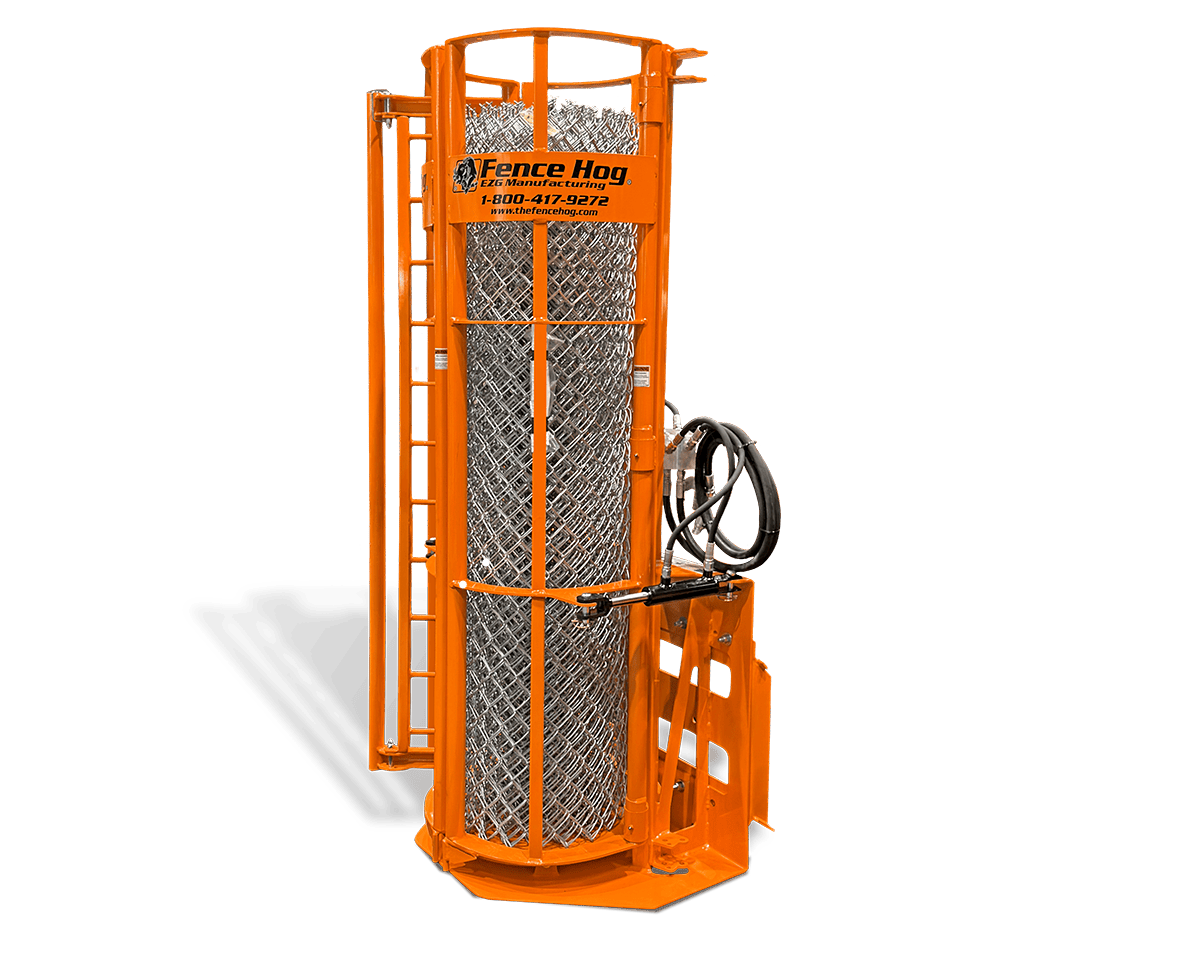
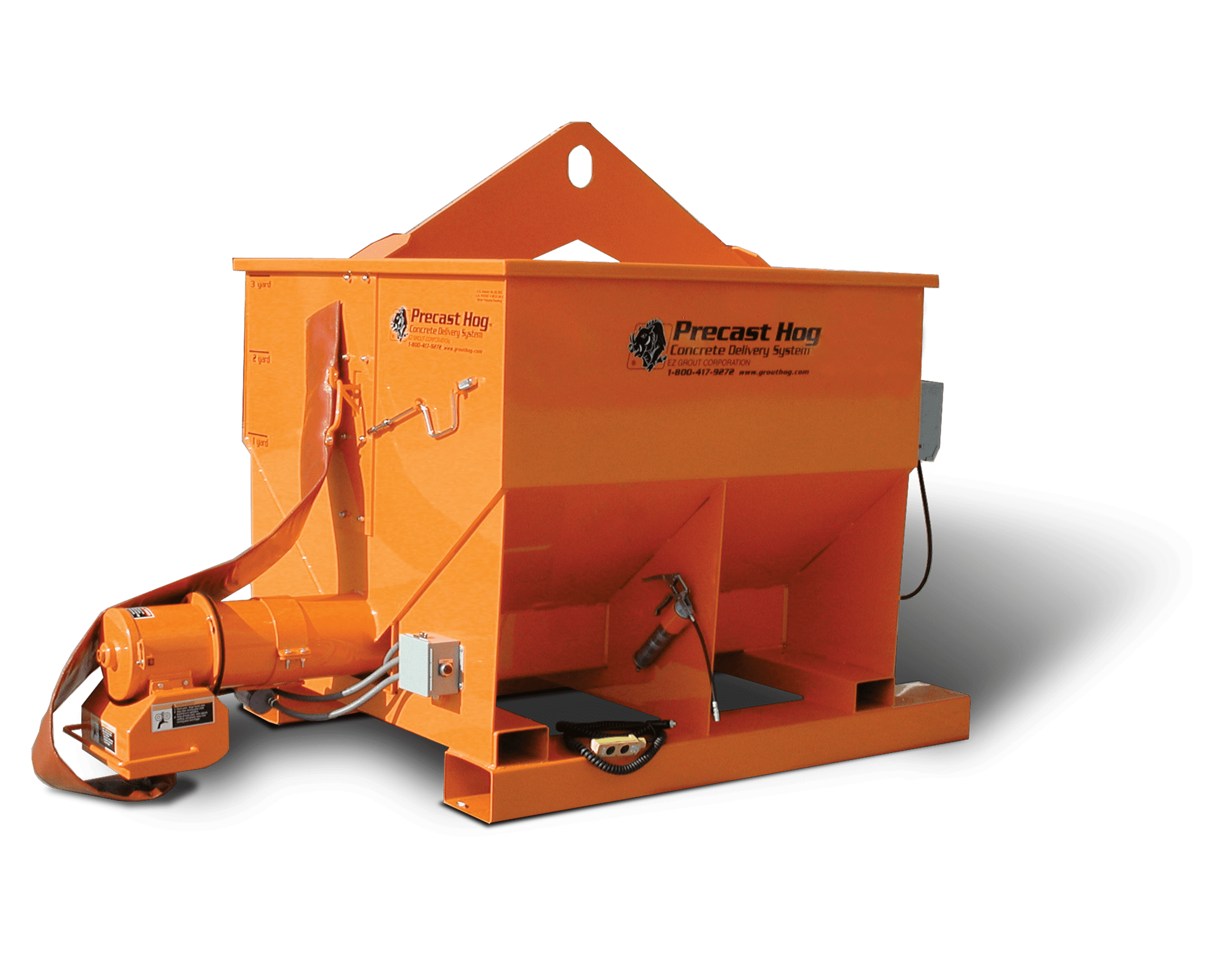
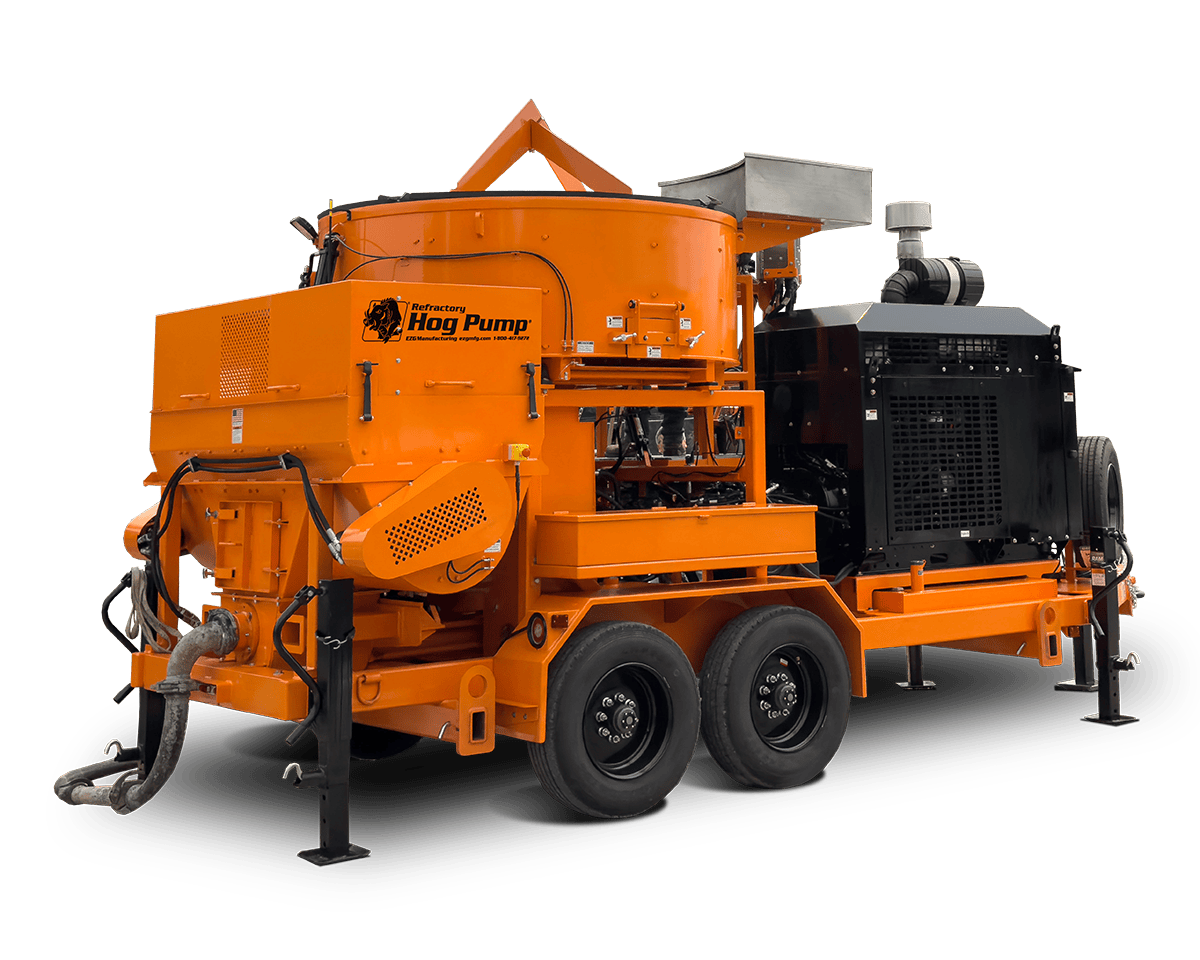
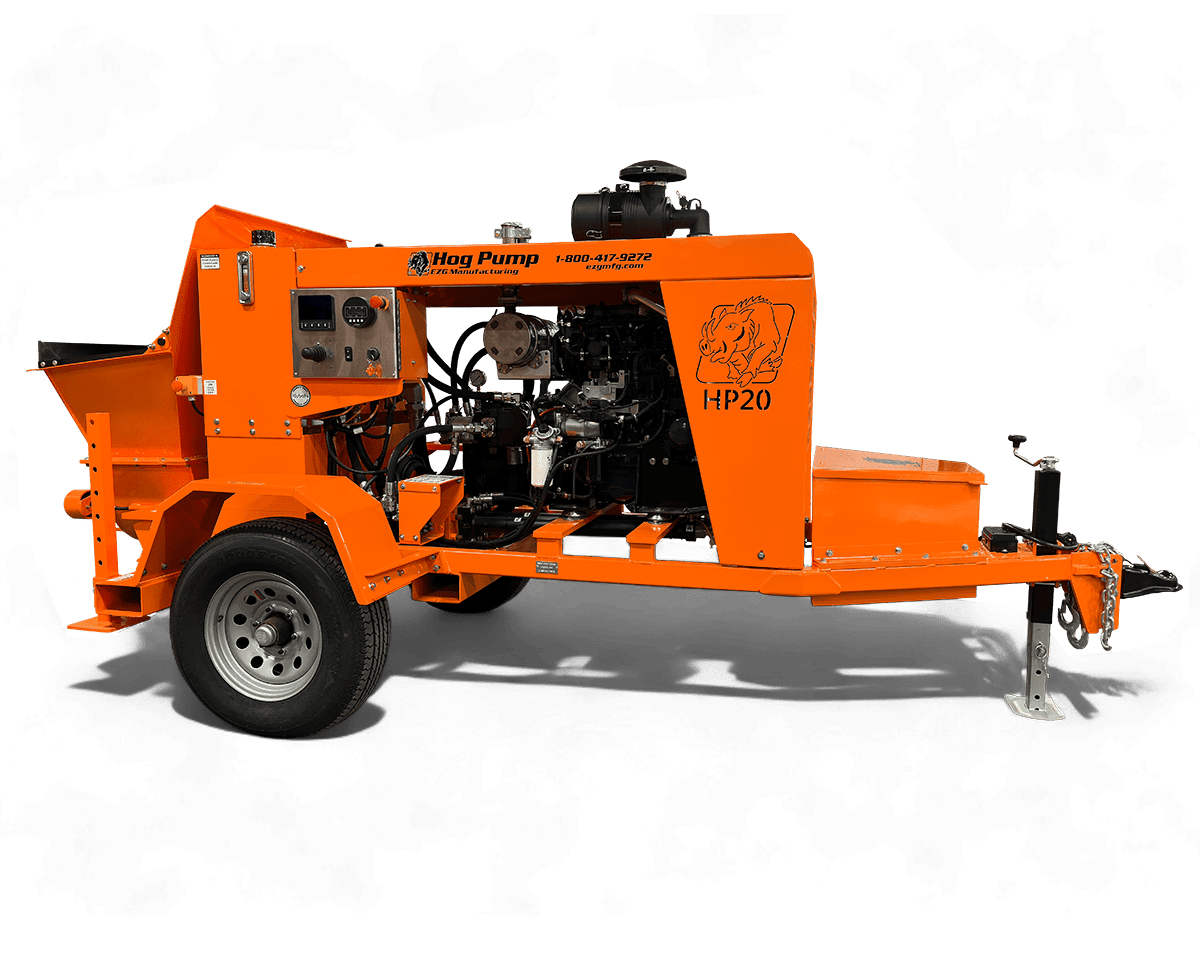
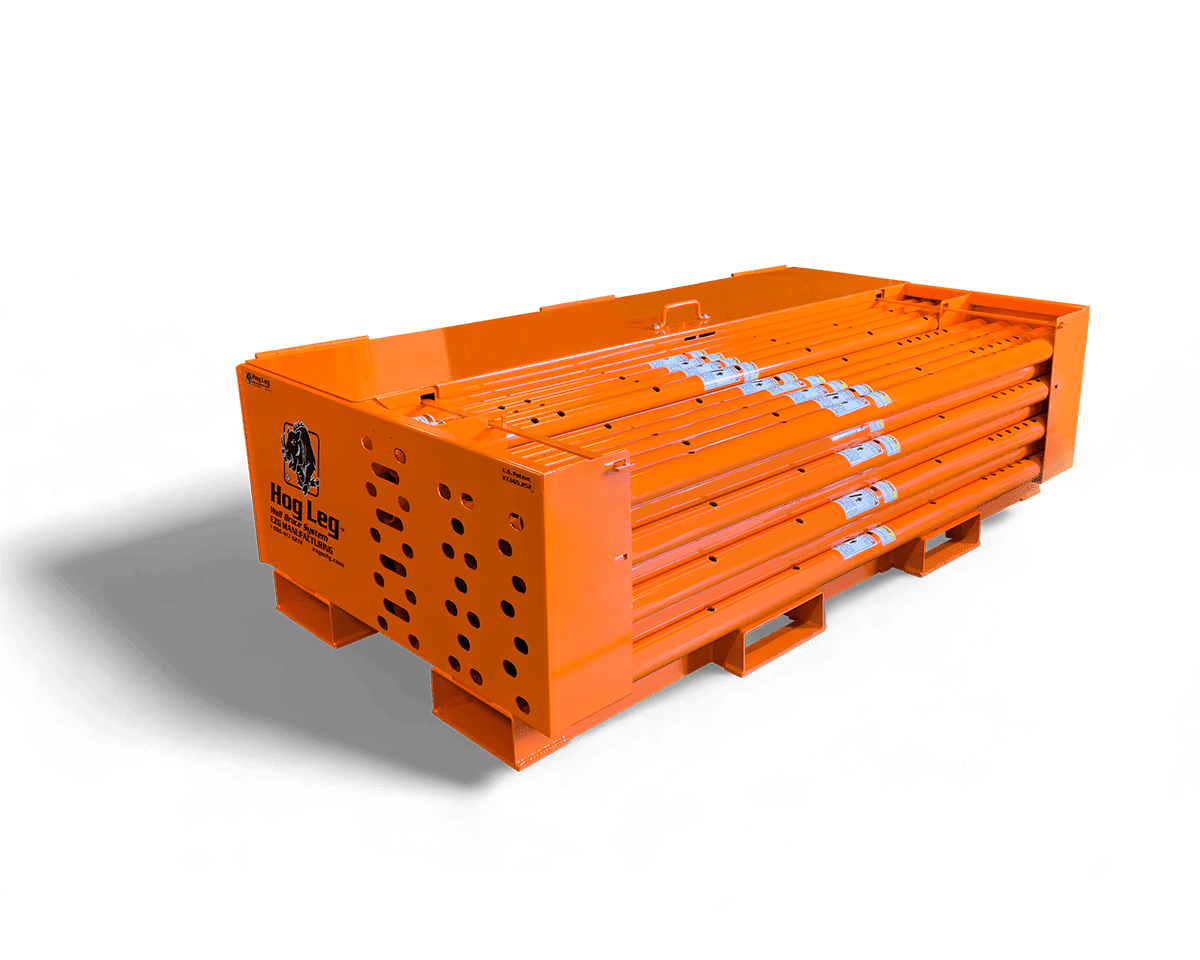
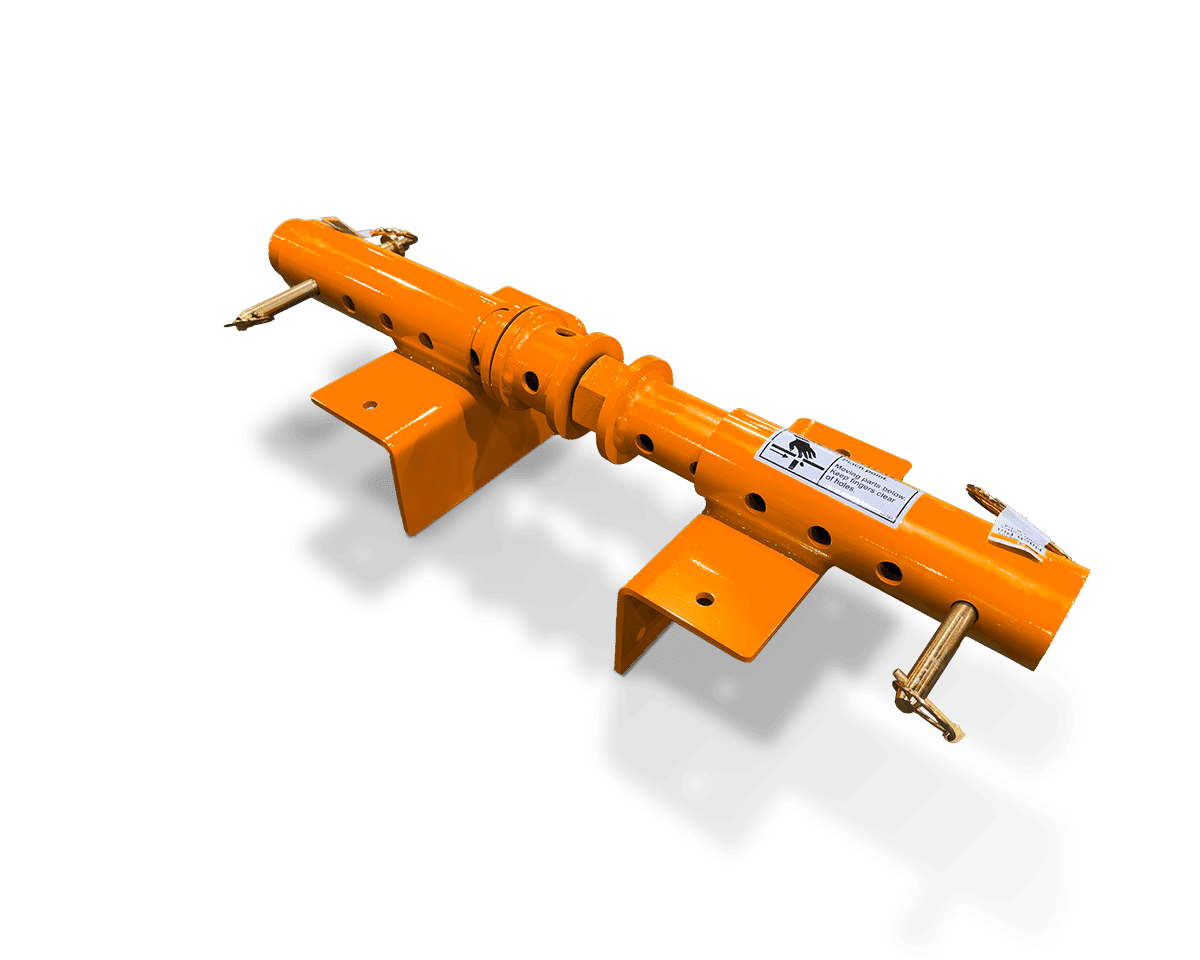
Sheet metal assembly involves joining multiple metal parts to create a finished product or components. Whether you’re building a rugged piece of industrial equipment or assembling a compact enclosure for electronic systems, the method of assembly plays a role in durability, cost, and lead time.
At EZG Manufacturing, we work with businesses that need more than just parts; they need fully assembled solutions. Backed by decades of experience and equipped with advanced fabrication tools, we provide everything from precision cutting to finished assemblies.
Below, we break down the most common sheet metal assembly techniques, how they’re used, and where they provide the most value.
What Is Sheet Metal Assembly?
Sheet metal assembly is the process of taking cut and formed metal components and fastening them together using various techniques. These parts can range from flat patterns to fully shaped brackets, panels, or structural elements. The goal is to turn individual sheet metal components into a reliable final product.
Different projects require different techniques depending on the material (such as carbon steel or stainless steel), the assembly environment (from aircraft assembly facilities to construction sites), and functional needs like weight, part count, or corrosion resistance.
From Flat Sheet to Final Form: Common Sheet Metal Assembly Techniques
1. Welding Techniques
Welding is one of the most reliable ways to assemble metal components. At EZG, we use both MIG and TIG welding to join parts depending on the thickness, material, and desired finish.
- MIG welding uses a continuously fed wire and shielding gas. It’s ideal for structural jobs and high-volume production.
- TIG welding uses a tungsten electrode and offers finer control. It’s best for stainless steel or components with visible seams where aesthetics matter.
Welding works by applying intense heat to melt the edges of the metal pieces, fusing them together as they cool and solidify. Each method creates a strong bond, often stronger than the base metal itself.
Our team includes AWS-certified welders and robotic welding systems for consistent results on both small and large batch orders.
2. Mechanical Fastening (Rivets, Bolts, Screws)
Mechanical fastening is often the preferred solution when:
- You need access to parts later
- Dissimilar metals are being joined
- Welding would cause thermal distortion or material issues
This method involves drilling or punching holes into parts and inserting hardware such as rivets, bolts, or sheet metal screws. These fasteners can create either permanent or removable joints, depending on the application.
- Rivets are ideal for permanent joints and commonly used in aerospace and transit industries.
- Bolts and screws allow for disassembly and are perfect for enclosures, inner fender assemblies, or components requiring regular maintenance.
At EZG, our technicians use assembly riveters, hand tools, and precision drilling to prepare threaded holes and mounting points, giving clients the flexibility they need in both prototyping and full production.
3. Adhesive Bonding
Adhesive bonding is a great option when welding or fasteners could interfere with aesthetics, introduce distortion, or aren’t compatible with certain materials. It’s commonly used to join:
- Thin sheet metal sections
- Dissimilar materials (like metal to plastic)
- Panels needing smooth finishes without visible fasteners
This method involves applying industrial adhesive or epoxy between surfaces, which is then cured using time, heat, or pressure to form a durable bond. Adhesives also distribute stress more evenly across the bonded area, making them well-suited for lightweight or vibration-prone designs.
While not the solution for every project, adhesive bonding is ideal for custom applications that demand flexibility or uniform stress distribution.
4. Hemming and Folding
Hemming is the process of folding the edge of a sheet metal part over itself to create a rounded, reinforced edge. This not only improves strength and safety but also offers a cleaner appearance than raw edges.
Using a press brake or hemming tool, we perform:
- Open hems for lighter-duty strength
- Closed hems for increased rigidity and alignment
This technique is frequently used in:
- Automotive manufacturing
- Appliance housings
- Flat pattern assemblies
Hemming helps reduce sharp edges, increase stiffness, improve multi-panel alignment, and even reduce part count, making it a cost-effective way to prep components for final assembly.
5. Tab and Slot Assembly
This technique uses precisely cut tabs and slots to lock parts together before final fastening. It’s often paired with welding or bonding and is:
- Fast to assemble
- Great for alignment and fixturing
- Ideal for laser cutting applications
Tabs fit tightly into slots, holding components together during final assembly and reducing the need for clamps or jigs. This self-fixturing approach is especially helpful in projects requiring high repeatability or tight tolerances.
Thanks to EZG’s in-house laser cutting capabilities, we frequently use this method to speed up assembly time, particularly for high-volume or repeat builds.
6. Clinching (Press Joining)
Clinching mechanically interlocks two layers of sheet metal without any added hardware or heat. Using a punch and die, it forms a dimple that locks the metals together.
Benefits include:
- No thermal distortion
- Tight, corrosion-resistant joints
- Minimal surface preparation
Clinching is often used in:
- HVAC systems
- Automotive subassemblies
- Sheet metal enclosures with high part counts
This technique is ideal when speed, cleanliness, and cost-efficiency are key concerns.
7. Stud Insertion and PEM Fasteners
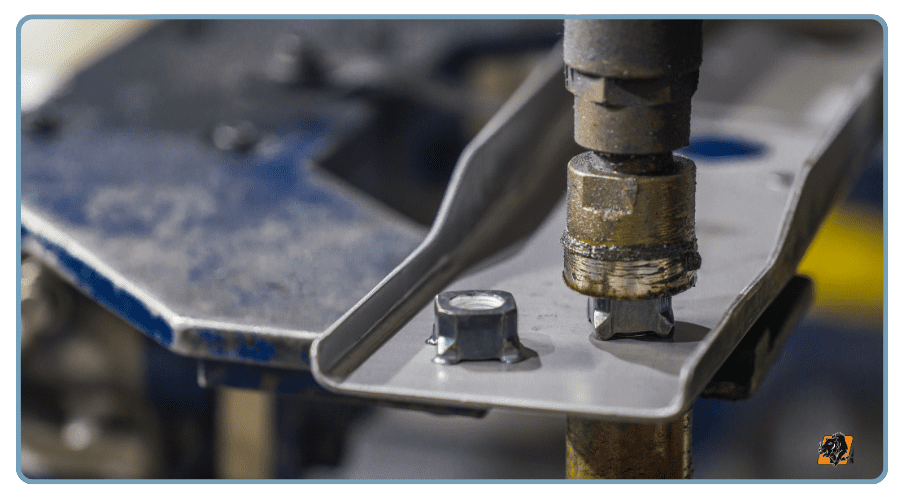

When your project needs components that mount circuit boards, covers, or brackets, stud and PEM fasteners provide reliable threaded attachment points.
We insert PEM studs, standoffs, and nuts directly into metal sheet parts before final assembly.
These are used in:
- Electromechanical assemblies
- Control panels
- Machine enclosures
Our CNC presses support high-speed insertion and consistent placement across parts, helping you maintain tolerances and fit.
8. Modular and Electromechanical Assembly
Modern designs often combine sheet metal parts with electronics, wiring, or plastic elements. EZG’s team supports complete electromechanical assembly, including:
- Mechanical buildout from flat pattern to box
- Wire routing and subcomponent mounting
- Integration of access panels, connectors, and fasteners
The process includes mounting PCBs, connecting wires to terminals, and installing hardware, all within metal enclosures fabricated in-house. This eliminates the need to coordinate with separate vendors for mechanical and electrical integration.
This is a common need in fields like medical, construction technology, and industrial automation, where a single source for both fabrication and assembly reduces complexity.
9. Powder Coating and Finishing
Assembly isn’t complete until your parts are finished and ready for use. At EZG, we offer in-house powder coating and wet paint booths to meet your appearance, durability, or spec requirements.
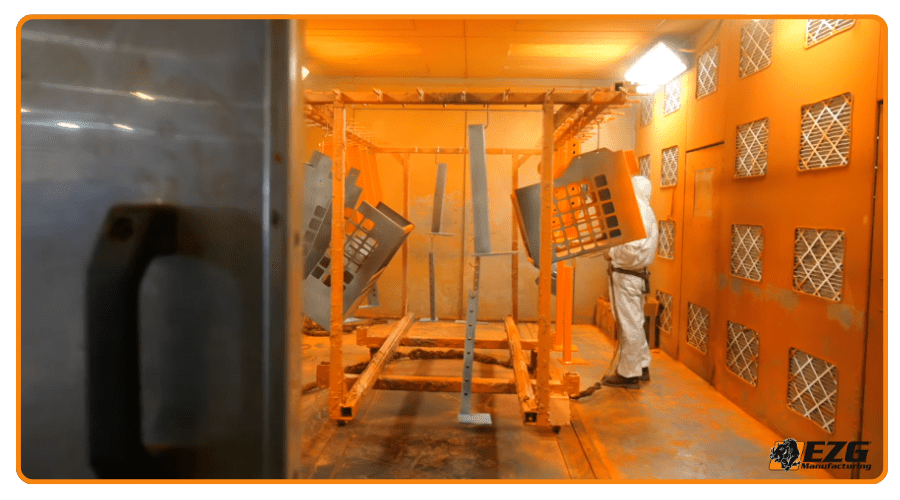

Powder coating involves spraying electrostatically charged powder onto metal surfaces, which is then cured in an oven to form a tough, uniform finish. It protects against corrosion and wear, and allows for consistent color and texture across production runs. Our finishing services help maintain the look and function of your sheet metal products from the inside out.
Benefits of in-house finishing services:
- Eliminate the need to transport parts between vendors
- Speed up the assembly process
- Protect sheet metal products from corrosion or wear
This full-service model saves time and helps maintain quality throughout the entire production cycle.
Choosing the Right Sheet Metal Assembly Technique
Choosing the best assembly method depends on:
- Material type (carbon steel, aluminum, stainless steel)
- Application requirements (load, vibration, temperature)
- Production volume (prototypes, short runs, or high-volume production)
- Design complexity and part access needs (access requirements, part geometry)
At EZG, our engineers assist with design reviews and can adapt sheet metal designs to suit faster production or easier assembly.
Why Work with EZG Manufacturing?
EZG Manufacturing isn’t just a fabrication shop, we’re a complete production partner. With over 120,000 sq. ft. of manufacturing space, heavy lifting capabilities, and advanced tools like our 10k fiber laser and 350-ton brake press, we’re built for projects ranging from a single metal part to full complex assemblies. We handle everything from laser cutting and welding to finishing and custom property creation.
From flat pattern to final product, our goal is to give you one point of contact and a finished product that’s ready for use.
Let’s work together to bring your metal assembly project to life—contact us today.