What’s the best way to make something? Building it up or cutting it down?
This is the question at the center of modern manufacturing. Whether you’re shaping metal parts or creating complex designs from scratch, your manufacturing method affects everything: cost, speed, durability, and scalability. The two most widely used approaches, subtractive manufacturing and additive manufacturing, take fundamentally different paths to the same goal: producing functional, reliable parts.
This guide breaks down both processes to help you make the right call.
What Is Subtractive Manufacturing?
Subtractive manufacturing is a material removal process. It starts with a solid block of material, usually metal or plastic, and uses a cutting tool to carve out the desired shape. It’s a traditional machining method and is widely used in today’s industrial settings due to its accuracy and versatility.
This subtractive process is well-suited for high-strength parts and high-volume production. Because the material is physically removed from a larger piece, it offers tight tolerances, smooth finishes, and material consistency.
Common Subtractive Manufacturing Techniques:
- CNC Milling Machine: controlled by numerical control software, it removes material in layers
- Turning (Lathes): spins the workpiece while a stationary tool cuts it
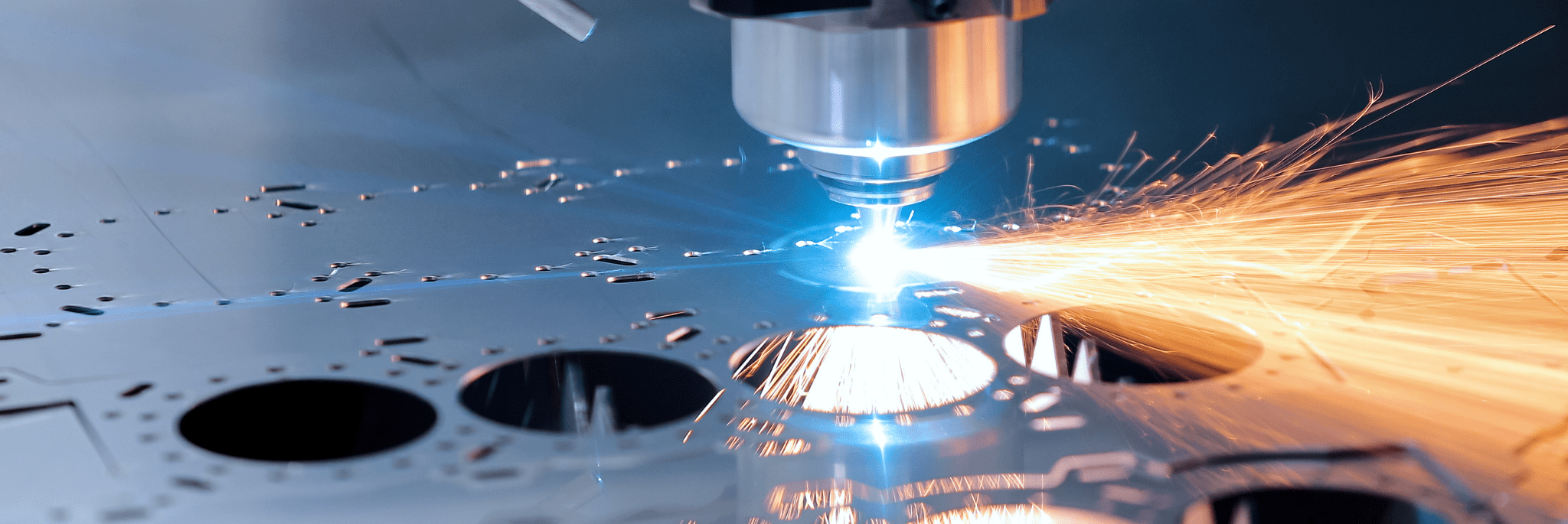
- Laser Cutting: uses high-speed lasers to slice through sheet metal
- Waterjet Cutting: a high-pressure stream cuts materials without heat
- Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM): uses electrical discharges to shape hard metals
Each subtractive manufacturing method offers specific benefits depending on material type, precision needs, and production volume.
Subtractive Manufacturing Process in Action
| Subtractive Technique | Description | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| CNC Milling | Layer-by-layer removal with rotating tools | High-precision metal parts |
| Laser Cutting | Melts material along a controlled path | Sheet metal fabrication |
| Turning (Lathe) | Creates symmetrical, rounded shapes | Shafts, bushings, flanges |
| EDM (Electrical Discharge) | Sparks erode conductive material | Hardened tool steel, dies |
What Is Additive Manufacturing?
Additive manufacturing builds objects layer by layer. Instead of starting with a block and removing material, it uses additive processes to construct the desired shape from nothing. This manufacturing technique is often referred to as 3D printing technology, though that’s just one part of it.
Unlike traditional machining, additive starts from nothing, allowing the creation of complex shapes and internal geometries that would be impossible or cost-prohibitive with a subtractive manufacturing method.
Common Additive Manufacturing Technologies:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): melts thermoplastics through a heated nozzle
- Stereolithography (SLA): uses light to cure resin layer by layer
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): fuses powdered materials with a laser
- Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS): builds metal parts using a laser and powdered metal
These additive manufacturing techniques are best suited for complex shapes, lightweight components, and rapid prototyping.
Additive Manufacturing Use Cases
- Custom prosthetics and implants
- Lightweight aerospace components
- Prototype iterations
- Low-run plastic part production
Additive is commonly used in R&D, industrial design, and custom manufacturing due to its design flexibility.
Additive vs Subtractive Manufacturing: Quick Comparison
| Factor | Subtractive Manufacturing | Additive Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Material removal from a solid block | Adds material layer by layer |
| Design Flexibility | Limited by tool paths | Ideal for complex geometries |
| Tolerances & Finish | High precision and smooth finish | May require post-processing |
| Speed (for prototypes) | Slower due to setup | Faster for one-off iterations |
| Material Waste | Higher due to cut-away material | Lower waste due to precise layering |
| Materials | Wide range: metals, plastics, alloys | Mostly plastics, select metal powders |
| Production Volume | Suited for high-volume runs | Best for small-scale production |
| Part Strength | Excellent for metal parts | Depends on additive technology |
When Should You Use Subtractive Manufacturing?
Subtractive methods are ideal when parts need to be durable, uniform, and reliable, especially in industrial and regulated environments.
Use the subtractive process when:
- You need tight tolerances or smooth finishes
- Parts must withstand stress or heat
- You’re working with hardened metals or specialty alloys
- You’re manufacturing at scale and need repeatability
Industries That Rely on Subtractive Machining:
- Aerospace
- Automotive
- Heavy Equipment
- Tool & Die
- Structural Fabrication
The subtractive manufacturing process also allows better integration with inspection tools and metrology, making it highly reliable for regulated applications.
When Should You Use Additive Manufacturing?
Additive processes make sense when the design is highly customized, lightweight, or intended for testing.
Turn to additive manufacturing for:
- Quick design iterations
- Customized, one-off parts
- Lightweight internal geometries
- Prototypes that don’t require structural strength
Additive is useful for engineers during the design phase when making complex shapes would be difficult with traditional machining.
Limitations of Additive Technology:
- Material selection is limited compared to conventional machining
- Surface finish often requires sanding or machining
- High-end machines can be costly
- Less reliable for high-stress, high-heat applications
What About Hybrid Manufacturing?
Hybrid manufacturing blends the strengths of both subtractive and additive methods. Typically, a part is 3D-printed to create complex internal structures, then finished with subtractive tools for flatness, tolerances, or mating surfaces.
Example: A heat exchanger is printed using additive technology to form internal channels, then machined to add threaded holes, mounting flanges, or high-precision surfaces.
This approach is gaining popularity for:
- Complex aerospace and medical parts
- Repairing worn metal components
- Advanced tooling applications
By combining a material removal process with an additive technique, manufacturers improve performance while reducing secondary operations and lead time.
How EZG Uses Subtractive Manufacturing Technology
At EZG Manufacturing, subtractive methods are the backbone of our custom fabrication services. We specialize in the subtractive manufacturing technology that delivers durable, high-quality parts on time.
In-house equipment includes:
- MAAC 10K Fiber Laser: fast, precise cutting tool for metals
- Cincinnati Brake Press (16′ bed): handles large metal bends
- CNC Machining Centers: for small parts or large metal parts up to 40 feet
- AWS-Certified Welding: MIG, TIG, robotic cells for volume work
- Powder Coating Booths: final finish without needing third-party vendors
Whether you’re sourcing brackets, racks, machine bases, or industrial components, our machining process is tailored to deliver reliable results. And we do it all under one roof.
Ready to Start?
Have a project in mind? Contact EZG Manufacturing to request a quote or talk to our team about your fabrication needs. Our expert team helps you choose the right manufacturing technique based on your goals, timeline, and material.